Here is another informative and in-depth article on network security.
Welcome to the world of network security, where understanding and implementing effective measures to protect against cyber threats is crucial. This article is specifically designed for beginners, providing a clear and concise overview of the various types of network security threats and the measures that can be used to protect against them.
Let's dive into a comprehensive guide on network security 101.
I. Introduction
A. Definition of Network Security
Network security refers to the protection of a computer network and its components, such as devices, data, and traffic, from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. It includes a variety of technologies, tools, and practices that are used to protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of a network and its resources.
B. Importance of Network Security
Network security is important because it helps to protect sensitive and confidential information from being accessed or stolen by unauthorized individuals or entities. This can include personal information, financial data, and other sensitive information that can be used for identity theft or financial fraud. Additionally, network security helps to protect against attacks that can disrupt the availability of a network, such as a denial of service attack. This can affect lost productivity and profit.
In short, network security is crucial to protect organizations and individuals from a wide range of cyber threats and to safeguard their sensitive and confidential information.
II. Types of Network Security
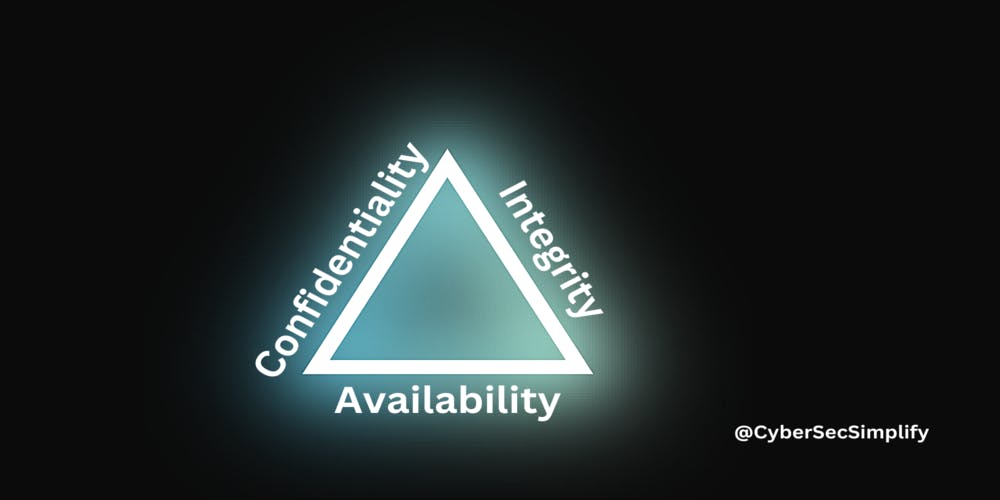
A. Confidentiality
Confidentiality in network security refers to the protection of sensitive and confidential information from unauthorized access or disclosure. This includes the use of encryption and access controls to prevent unauthorized individuals from viewing or stealing sensitive information. Confidentiality is important to protect personal information, financial data, and other sensitive information that can be used for identity theft or financial fraud.
B. Integrity
Integrity in network security refers to the protection of data and network resources from unauthorized modification or destruction. This includes the use of digital signatures and hash functions to ensure that data has not been tampered with and remains in its original form. Integrity is important to ensure that data is not altered or corrupted during transmission and that it can be trusted as an accurate representation of the original information.
C. Availability
Availability in network security refers to the ability of authorized users to access network resources and data when needed. This includes protecting against attacks that can disrupt the availability of a network, such as a denial of service attack. It also includes ensuring that network resources and data are always accessible to authorized users, even in the event of a disaster or other disruptive event. Availability is important to ensure that networks and services are always available and can be accessed by authorized users when needed.
III. Network Security Threats

A. Malware
Malware is a type of software that is designed to harm or exploit a computer or network. This can include viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, and other types of malicious software. Malware can be used to steal sensitive information, disrupt network availability, or take control of a computer or network.
B. Phishing
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack that is used to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial information. This is often done through the use of email or text messages that appear to be from a legitimate source, such as a bank or other financial institution. These messages may contain links to fake websites or ask for personal information to be entered into a form.
C. Denial of Service (DoS)
A denial of service (DoS) attack is an attempt to make a network or service unavailable to its intended users. This can be done by overwhelming a network or service with a large amount of traffic or by exploiting vulnerabilities in a network or service. This can result in lost productivity and revenue.
D. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM)
A man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack is a type of attack in which an attacker intercepts and alters communications between two parties. This can be done by intercepting network traffic or by exploiting vulnerabilities in a network or service. This can result in the alteration or theft of sensitive information.
E. Social Engineering
Social engineering is a type of attack that relies on tricking individuals into revealing sensitive information or performing actions that can harm a network or service. This can include phishing, vishing (voice phishing), and pretexting (creating a false identity to gain trust). Social engineering attacks can be used to steal sensitive information or gain unauthorized access to a network or service.
IV. Network Security Measures
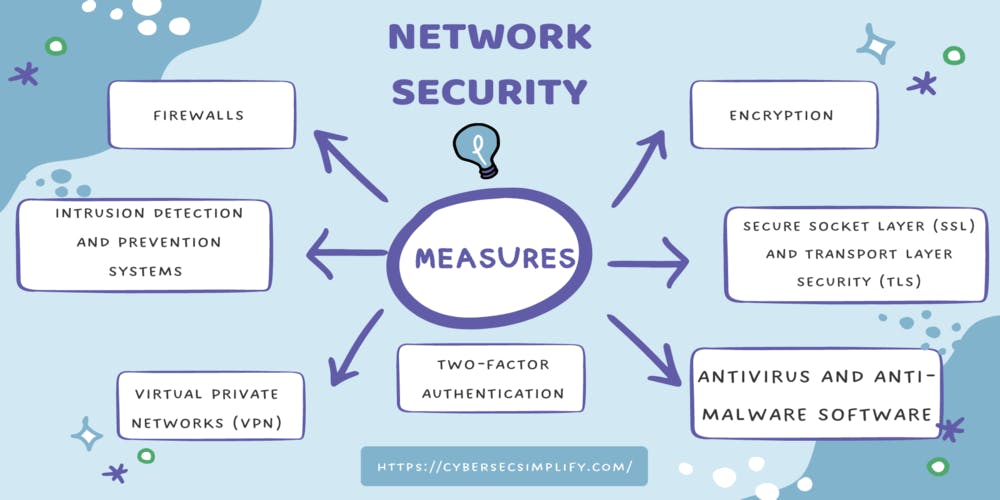
A. Firewalls
A firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls incoming and gregarious network business grounded on destined security rules and programs. Firewalls can be hardware- or software-based and can be used to block unauthorized access, prevent unauthorized use, and protect against network-based threats.
B. Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
An Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDPS) is a network security system that monitors network traffic for signs of malicious activity and blocks unauthorized access. IDS and IPS can detect and prevent a wide range of cyber threats, including malware, phishing, and denial of service attacks.
C. Virtual Private Networks (VPN)
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a secure and private communication channel that is created over a public network, such as the internet. VPNs use encryption and other security measures to protect network traffic from being intercepted by unauthorized individuals or entities. VPNs can be used to protect sensitive and confidential information, such as login credentials and financial data, when it is transmitted over a public network.
D. Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS)
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) are protocols that are used to secure communications between a web server and a web browser. SSL and TLS use encryption to protect data from being intercepted by unauthorized individuals or entities. This is especially important when sensitive information, such as login credentials and financial data, is being transmitted over a public network.
E. Encryption
Encryption is the process of converting plain text into a code that can only be deciphered by authorized individuals or entities. Encryption can be used to protect sensitive and confidential information, such as login credentials and financial data, from being intercepted or stolen by unauthorized individuals or entities.
F. Antivirus and Anti-malware software
Antivirus and anti-malware software is designed to detect and remove malware from a computer or network. This can include viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, and other types of malicious software. Antivirus and anti-malware software can be used to protect against a wide range of cyber threats and to ensure the integrity and availability of network resources and data.
G. Two-factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is an additional layer of security in which a user is required to provide two forms of identification to access a network or service. This can include a combination of a password and a security token, a fingerprint, or facial recognition. 2FA helps to protect against unauthorized access and to ensure that only authorized individuals or entities can access sensitive and confidential information.
V. Network Security Best Practices
A. Keep software up-to-date
Keeping software up-to-date is an important best practice in network security. Software vendors regularly release updates and patches to fix known vulnerabilities and improve the security of their products. By keeping software up-to-date, organizations and individuals can reduce the risk of being exploited by cybercriminals who are looking to take advantage of known vulnerabilities.
B. Use strong passwords and change them regularly
Using strong passwords and changing them regularly is another important best practice in network security. Strong passwords are difficult to guess or crack and are essential in protecting against unauthorized access. Changing passwords regularly can help to further protect against unauthorized access, as it makes it more difficult for cybercriminals to use stolen or guessed passwords to gain unauthorized access.
C. Limit access to sensitive data
Limiting access to sensitive data is another important best practice in network security. By limiting access to sensitive data to authorized individuals or entities, organizations can reduce the risk of sensitive data being accessed or stolen by unauthorized individuals or entities. This can be done through the use of access controls and other security measures.
D. Regularly monitor and audit network activity
Regularly monitoring and auditing network activity is an important best practice in network security. By monitoring and auditing network activity, organizations can identify and respond to potential security threats and vulnerabilities. This can include monitoring for suspicious network traffic, such as traffic from known malicious IP addresses, and auditing network configurations and settings to ensure that they are secure.
E. Train employees on security best practices
Training employees on security best practices is an important best practice in network security. By providing employees with training on security best practices, organizations can help to ensure that employees are aware of potential security threats and can take appropriate measures to protect against them. This can include training on topics such as password security, phishing, and other cyber threats.
Here are some recommended books on the listed Network and Security :
Network Security Essentials: Applications and Standards Paperback -by William Stallings
VI. Conclusion
A. Recap of key points
In this article, we discussed the importance of network security and the various types of network security threats and measures that are used to protect against them. We also discussed best practices in network security, such as keeping software up-to-date, using strong passwords and changing them regularly, limiting access to sensitive data, regularly monitoring and auditing network activity, and training employees on security best practices.
B. Reminder of the importance of network security
It is important to remember that network security is crucial to protect organizations and individuals from a wide range of cyber threats and to safeguard their sensitive and confidential information. By understanding the types of network security threats and measures, and by implementing best practices in network security, organizations and individuals can help to protect themselves from cyber threats and ensure the security and integrity of their networks and data.
This post contains affiliate links. If you use these links to buy something we may earn a commission. Thanks.
We thank you for reading this article and hope it provided you with valuable information. We encourage you to follow and support our cybersecsimplify community for more informative and in-depth articles on cybersecurity.

